This question explores the concept of animal migration.
How do animals and birds migrate, and why do they travel to different places?
پاسخ ها: {{ repliesNum }}
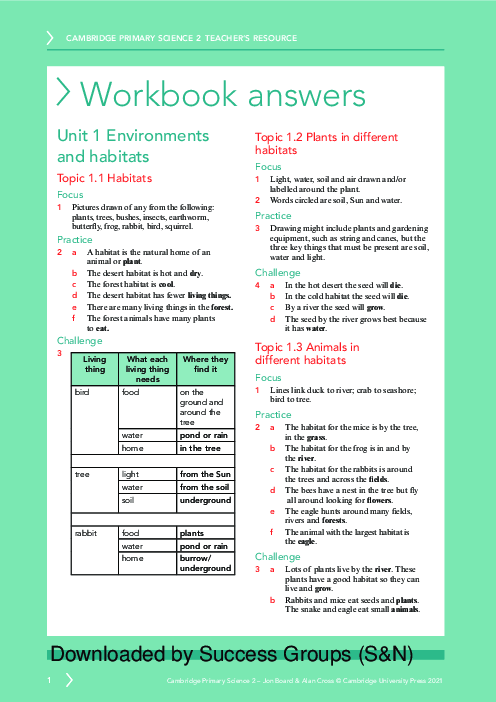
پاسخ انتخاب شده
در پاسخ به: {{ reply.reply_to.name }}
در پاسخ به
این پیام حذف شده است.