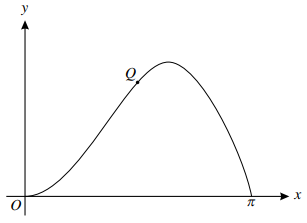
The diagram shows the curve $y = x\sin x$, for $0 \leqslant x \leqslant \pi $. The point $Q\left( {\frac{1}{2}\pi ,\,\,\frac{1}{2}\pi } \right)$ lies on the curve.
a) Show that the normal to the curve at $Q$ passes through the point $(\pi ,{\text{ }}0)$
b) Find $\frac{d}{{dx}}(\sin x - x\cos x)$.
c) Hence evaluat $\int_0^{\frac{1}{2}\pi } {x\sin x\,dx} $.
پاسخ تشریحی :
تحلیل ویدئویی تست
منتظریم اولین نفر تحلیلش کنه!