A Level Chemistry PowerPoint Presentation | Carboxylic Acids
2. Scientific Keywords - Carboxyl Group, pKa, Hydrogen Bonding, Solubility, Reactivity, Synthesis
3. Main Indicators - Structural Formulas, Physical Properties, Reaction Mechanisms, Spectroscopic Analysis, Industrial Applications, Biological Roles
4. Goals - Understanding carboxylic acid properties, Identifying functional groups, Analyzing reactivity and synthesis, Exploring applications in organic chemistry, Investigating biological significance, Developing laboratory skills
5. Expectations - Mastery of carboxylic acid nomenclature, Ability to predict physical and chemical properties, Proficiency in reaction mechanisms, Application of theoretical concepts, Engagement in practical experiments, Development of analytical reasoning
6. Content Indicators - Definitions and classifications, Reaction examples, Mechanistic pathways, Experimental procedures, Real-world applications, Assessment questions and practice problems
ارسال شده توسط این معلم:
UNIT 1: Atomic structure
1.1 Particles in the atom and atomic radius
1.2 Isotopes
1.3 Electrons‚ energy levels and atomic orbitals
1.4 Ionisation energy
UNIT 2: Atoms‚ molecules and stoichiometry
2.1 Relative masses of atoms and molecules
2.2 The mole and the Avogadro constant
2.3 Formulae
2.4 Reacting masses and volumes (of solutions and gases)
UNIT 3: Chemical bonding
3.1 Electronegativity and bonding
3.2 Ionic bonding
3.3 Metallic bonding
3.4 Covalent bonding and coordinate (dative covalent) bonding
3.5 Shapes of molecules
3.6 Intermolecular forces‚ electronegativity and bond properties
3.7 Dot-and-cross diagrams
UNIT 4: States of matter
4.1The gaseous state: ideal and real gases and pV = nRT
4.2 Bonding and structure
UNIT 5: Chemical energetics
5.1 Enthalpy change‚ ΔH
5.2 Hess’s Law
UNIT 6: Electrochemistry
6.1 Redox processes: electron transfer and changes in oxidation number (oxidation state)
UNIT 7: Equilibria
7.1 Chemical equilibria: reversible reactions‚ dynamic equilibrium
7.2 Bronsted–Lowry theory of acids and bases
UNIT 8: Reaction kinetics
8.1 Rate of reaction
8.2 Effect of temperature on reaction rates and the concept of activation energy
8.3 Homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts
UNIT 9: The Periodic Table: chemical periodicity
9.1 Periodicity of physical properties of the elements in Period 3
9.2 Periodicity of chemical properties of the elements in Period 3
9.3 Chemical periodicity of other elements
UNIT 10: Group 2
10.1 Similarities and trends in the properties of the Group 2 metals‚ magnesium to barium‚ and their compounds
UNIT 11: Group 17
11.1 Physical properties of the Group 17 elements
11.2 The chemical properties of the halogen elements and the hydrogen halides
11.3 Some reactions of the halide ions
11.4 The reactions of chlorine
UNIT 12: Nitrogen and sulfur
12.1 Nitrogen and sulfur
UNIT 13: An introduction to AS Level organic chemistry
13.1 Formulae‚ functional groups and the naming of organic compounds
13.2 Characteristic organic reactions
13.3 Shapes of Organic Molecules; σ & π Bonds
13.4 Isomerism: structural and stereoisomerism
14.1 Alkanes
UNIT 15: Halogen compounds
15.1 Halogenoalkanes
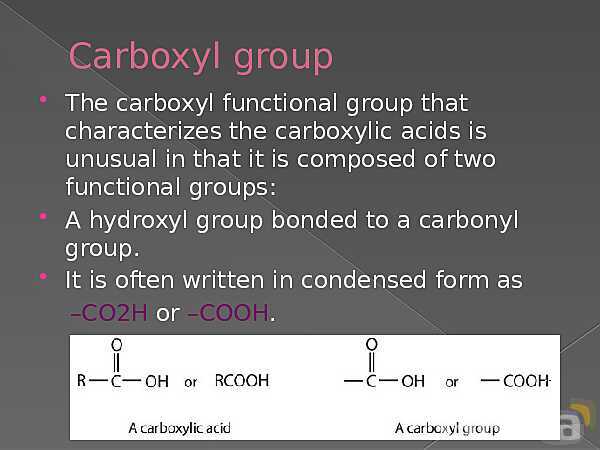
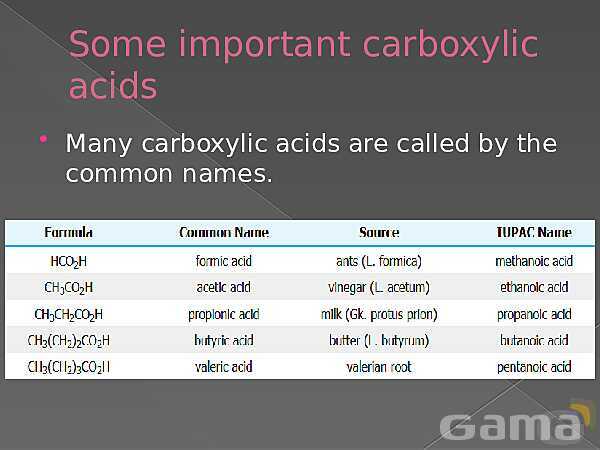
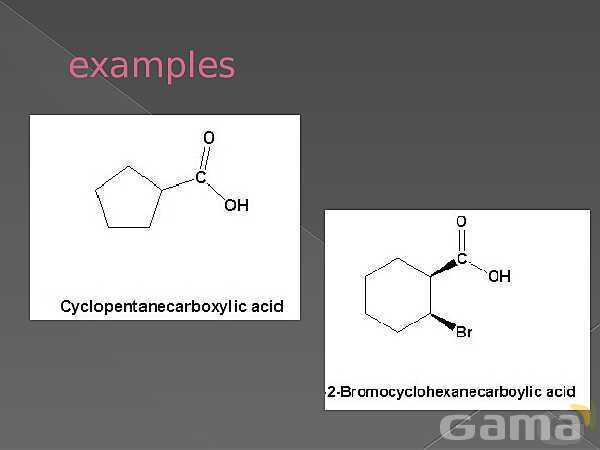
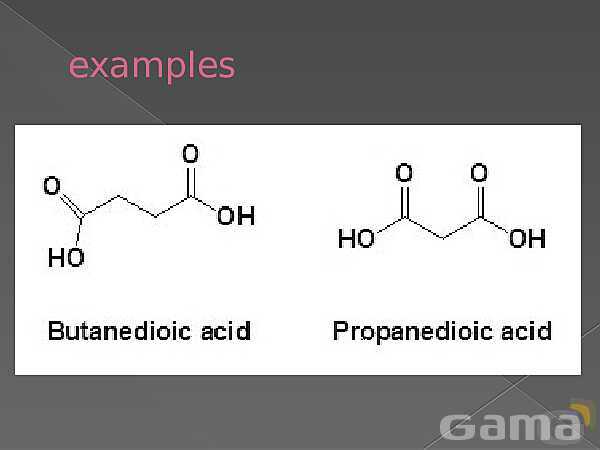
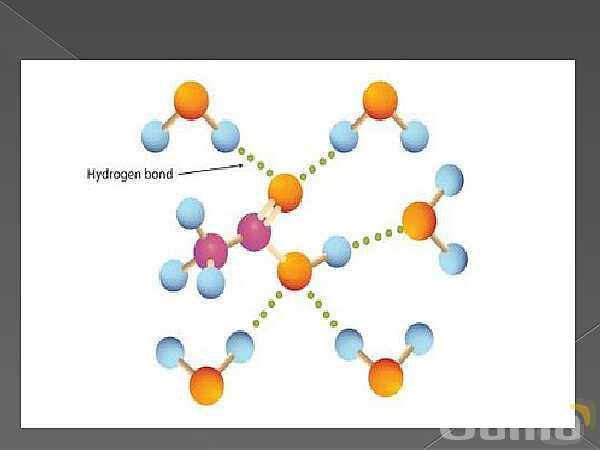
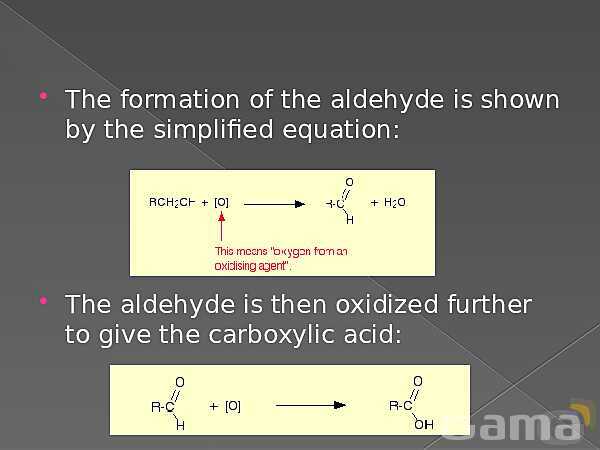
UNIT 18: Carboxylic acids and derivatives
UNIT 19: Nitrogen compounds
19.1 Primary amines
19.2 Nitriles and hydroxynitriles
UNIT 20: Polymerisation
20.1 Addition polymerisation
UNIT 21: Organic synthesis Analysis
21.1 Organic synthesis
UNIT 22: Analytical techniques
22.1 Infra-red spectroscopy
22.2 Mass spectrometry
UNIT 23: Chemical energetics
23.1 Lattice energy and Born-Haber cycles
23.2 Enthalpies of solution and hydration
23.3 Entropy change‚ ΔS
23.4 Gibbs free energy change‚ ΔG
UNIT 24: Electrochemistry
24.1 Electrolysis
24.2 Standard electrode potentials; standard cell potentials and the Nernst equation
UNIT 25: Equilibria
25.1 Acids and bases
25.2 Partition coefficients
UNIT 26: Reaction kinetics
26.1 Simple rate equations‚ orders of reaction and rate constants
26.2 Homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts
UNIT 27: Group 2
27.1 Similarities and trends in the properties of the Group 2 metals‚ magnesium to barium‚ and their compounds
UNIT 28: Chemistry of transition elements
28.1 General physical and chemical properties of the first row of transition elements, titanium to copper
28.2 General characteristic chemical properties of the first set of transition elements‚ titanium to copper
28.3 Colour of complexes
28.4 Stereoisomerism in transition element complexes
28.5 Stability constants‚ Kstab
UNIT 29: An introduction to A Level organic chemistry
29.1 Formulae‚ functional groups and the naming of organic compounds
29.2 Characteristic organic reactions
29.3 Shapes of Aromatic Organic Molecules; σ & π Bonds
29.4 Isomerism: optical
UNIT 30: Hydrocarbons
30.1 Arenes
UNIT 31: Halogen compounds
31.1 Halogen compounds
UNIT 32: Hydroxy compounds
32.1 Alcohols
32.2 Phenol
UNIT 33: Carboxylic acids and derivatives
33.1 Carboxylic acids
33.2 Esters
33.3 Acyl chlorides
UNIT 34: Nitrogen compounds
34.1 Primary and secondary amines
34.2 Phenylamine and azo compounds
34.3 Amides
34.4 Amino acids
UNIT 35: Polymerisation
35.1 Condensation polymerisation
35.2 Predicting the type of polymerisation
35.3 Degradable polymers
UNIT 36: Organic synthesis Analysis
36.1 Organic synthesis
UNIT 37: Analytical techniques
37.1 Thin-layer chromatography
37.2 Gas /liquid chromatography
37.3 Carbon-13 NMR spectroscopy
37.4 Proton (1 H) NMR spectroscopy



















باز نشر محتواها در فضای مجازی، ممنوع است.