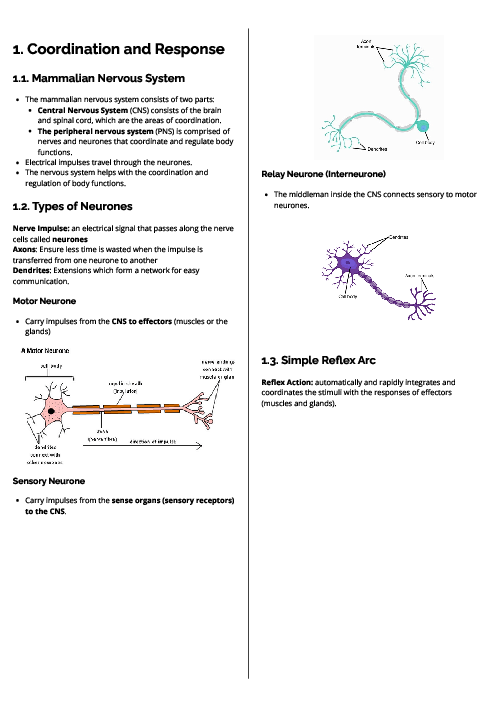
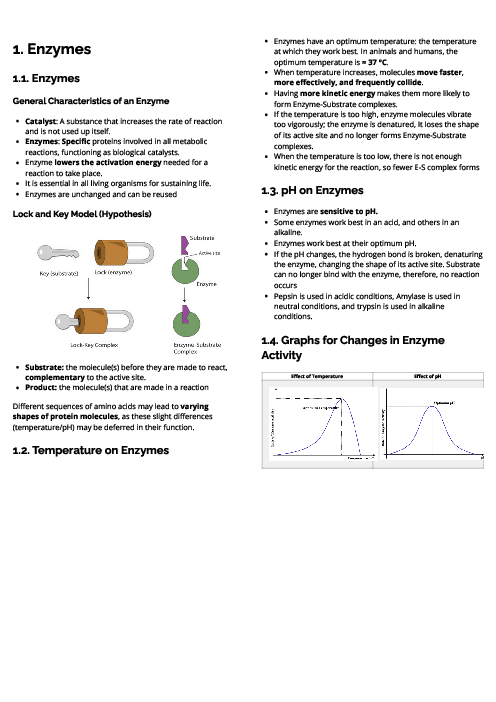
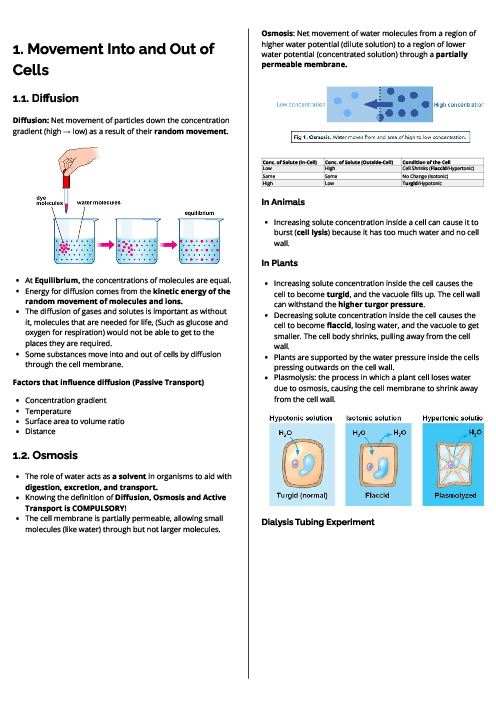
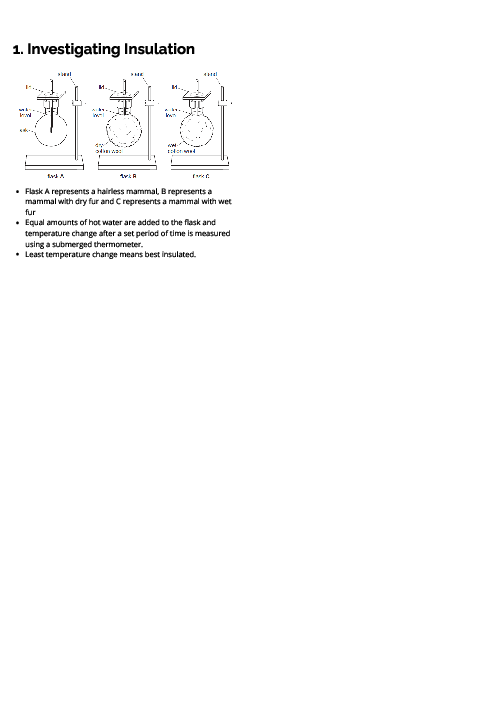
Biology (0610) Inheritancn Revision Note
This document explains inheritance for CAIE IGCSE Biology, covering chromosomes, genes, DNA, protein synthesis, and patterns of genetic transmission. Chromosomes are described as DNA structures carrying genes, with alleles as alternative forms of a gene. The difference between haploid and diploid nuclei is highlighted, along with how DNA bases determine amino acid sequences and protein structures. Protein synthesis is explained in two stages: transcription (DNA to mRNA) and translation (assembling amino acids into proteins at ribosomes). Cell division is covered with mitosis producing genetically identical cells for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction, and meiosis producing gametes with half the chromosome number, creating genetic variation. Monohybrid inheritance is explained using genotypes, phenotypes, dominance, and recessiveness, with Punnett squares and pedigree diagrams to trace traits and predict offspring probabilities. Ratios like 3:1 and 1:1 are demonstrated with examples such as eye colour and flower colour. Extensions of Mendelian genetics are included, covering codominance (e.g., red and white flowers producing patterned offspring) and the ABO blood group system as an example of codominance and multiple alleles. Sex-linked characteristics, particularly X-linked recessive disorders, are also explained as traits more common in males than females.
باز نشر محتواها در فضای مجازی، ممنوع است.

باز نشر محتواها در فضای مجازی، ممنوع است.