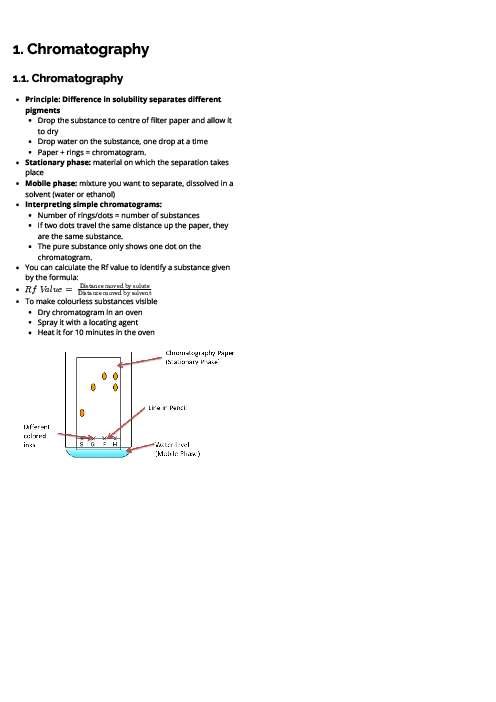
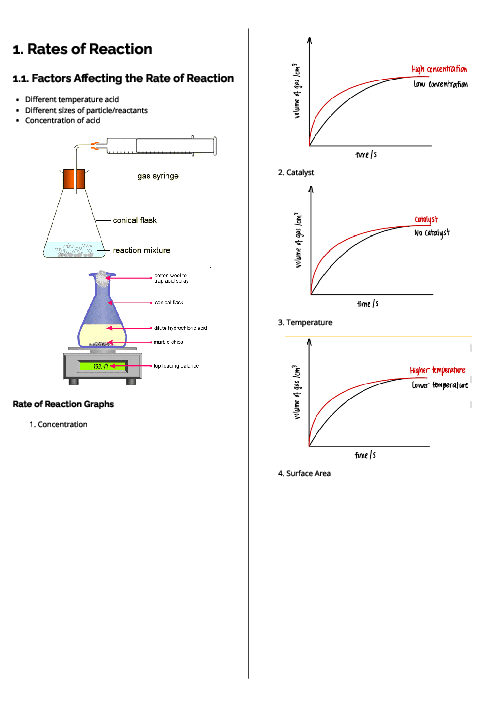
Chemistry (0620) Atoms, Elements and Compounds Revision Note
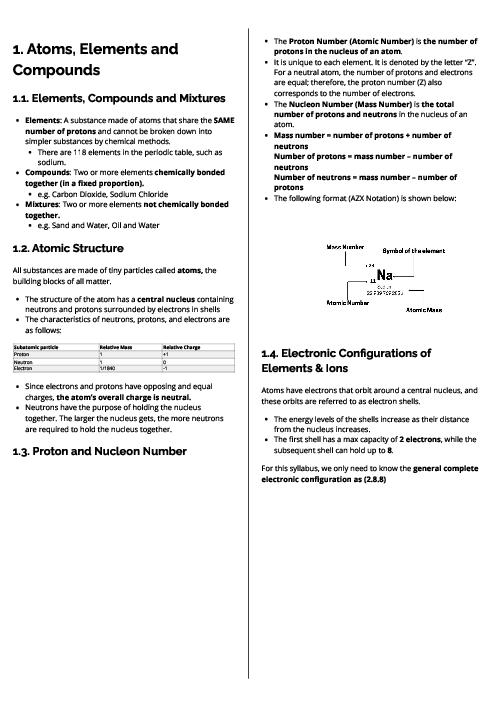
This document introduces atoms, elements, and compounds for CAIE IGCSE Chemistry, covering fundamental concepts of matter and bonding. It begins with the distinction between elements, compounds, and mixtures—elements contain identical atoms, compounds consist of chemically bonded elements in fixed ratios, and mixtures combine substances without bonding. Atomic structure is explained with protons, neutrons, and electrons, highlighting their charges, masses, and roles. The proton number (Z) defines the element, while the nucleon number (A) represents protons plus neutrons. Electronic configurations show how electrons are arranged in shells, linked to group and period numbers. Isotopes are described as atoms of the same element with different neutrons, sharing chemical properties but differing in physical properties. The calculation of relative atomic mass using isotope abundance is explained with examples. Bonding structures are then detailed: metallic bonding (positive ions in a sea of delocalised electrons), giant covalent structures like diamond, graphite, and silicon dioxide, and their unique properties. Covalent bonds in molecules and ionic bonds in giant lattices are described with diagrams, along with properties such as melting points, electrical conductivity, and brittleness. This guide equips students with the foundational knowledge of atomic theory and bonding essential for further chemistry topics.
باز نشر محتواها در فضای مجازی، ممنوع است.
باز نشر محتواها در فضای مجازی، ممنوع است.