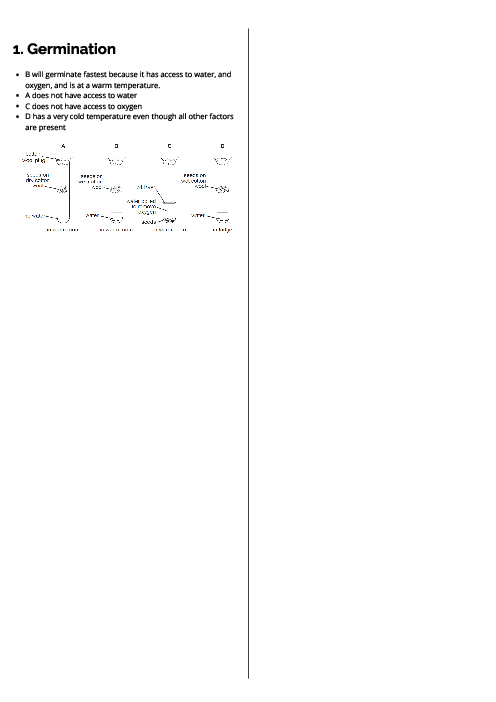
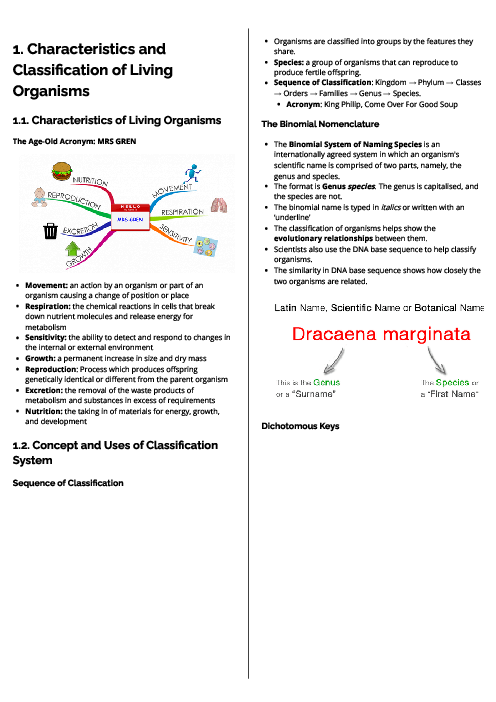
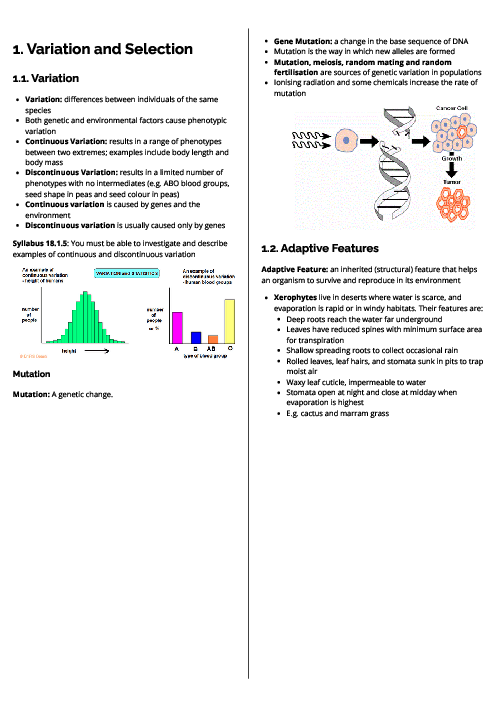
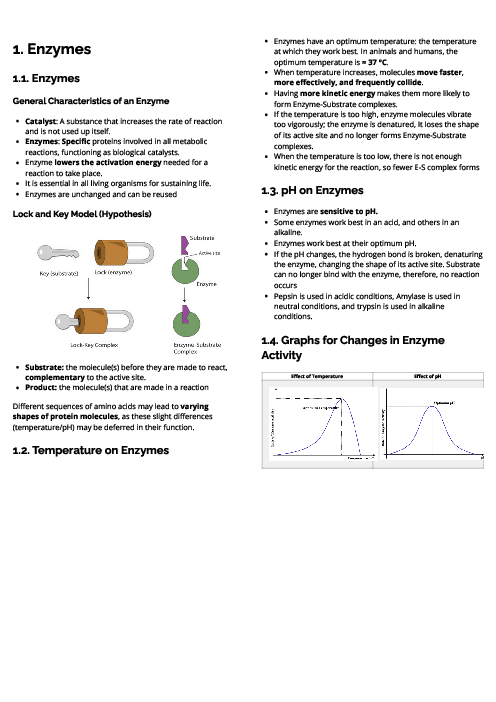
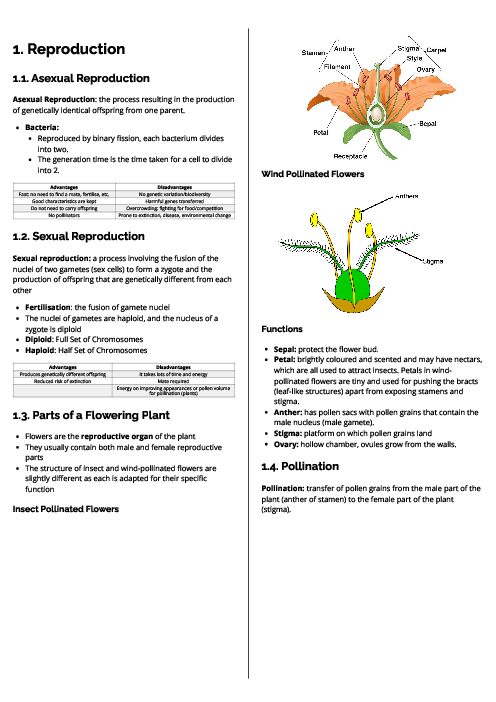
Biology (0610) Excretion in Humans Revision Note
Learn Biology (0610) Excretion in Humans with detailed notes on the kidneys, liver, urinary system, and removal of metabolic wastes. Designed for Cambridge IGCSE revision with clear explanations and essential exam concepts.
باز نشر محتواها در فضای مجازی، ممنوع است.
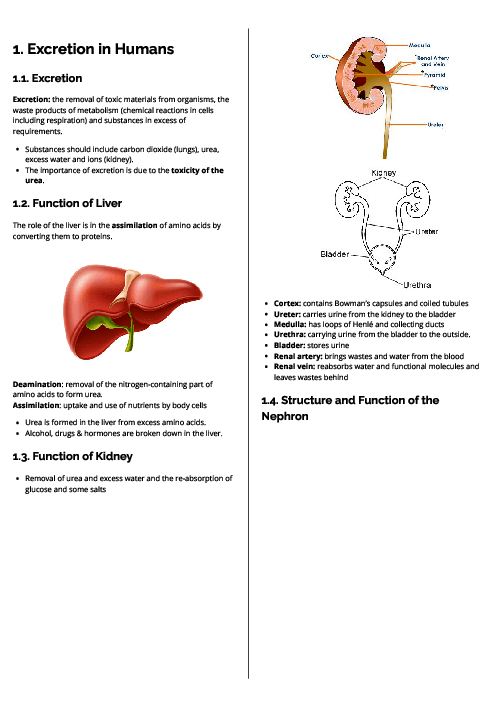
باز نشر محتواها در فضای مجازی، ممنوع است.