Chemistry (0620) Stoichiometry Revision Note
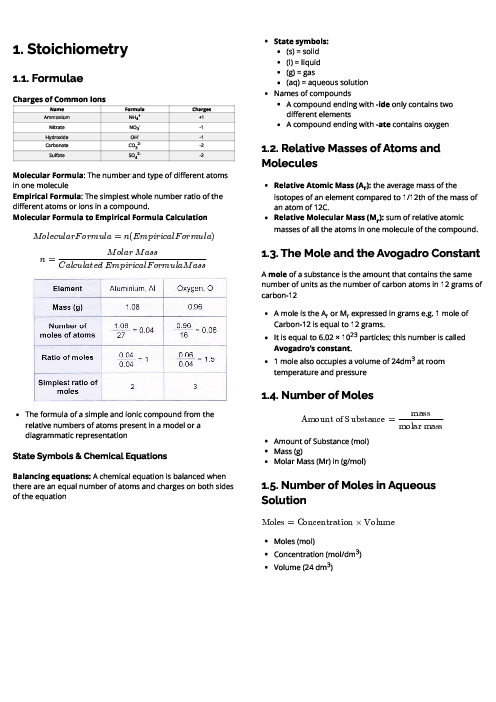
This document explains stoichiometry for CAIE IGCSE Chemistry, focusing on chemical formulae, mole calculations, and reaction yields. It begins with ionic charges and the distinction between molecular and empirical formulae, showing how to deduce formulas from atom ratios and models. State symbols and naming rules are introduced, explaining that compounds ending in “-ide” contain two elements, while “-ate” compounds include oxygen. The section on relative atomic mass (Ar) and relative molecular mass (Mr) outlines how to calculate masses from atomic composition. The mole concept is defined as the amount containing 6.02 × 10²³ particles, with 1 mole occupying 24 dm³ of gas at room temperature and pressure. Clear formulas link moles, mass, molar mass, concentration, and volume, with worked examples on aqueous solutions and gas volumes. Titration calculations demonstrate how to use concentration and volume to find moles and deduce unknowns. The document also covers percentage composition, percentage purity, and percentage yield, helping students analyse experimental results. By mastering these calculations, learners can balance equations, predict reactant and product quantities, and evaluate efficiency in chemical processes. This guide provides essential tools for accurate problem-solving in chemistry exams.
باز نشر محتواها در فضای مجازی، ممنوع است.
باز نشر محتواها در فضای مجازی، ممنوع است.