Chemistry (0620) Metals Revision Note
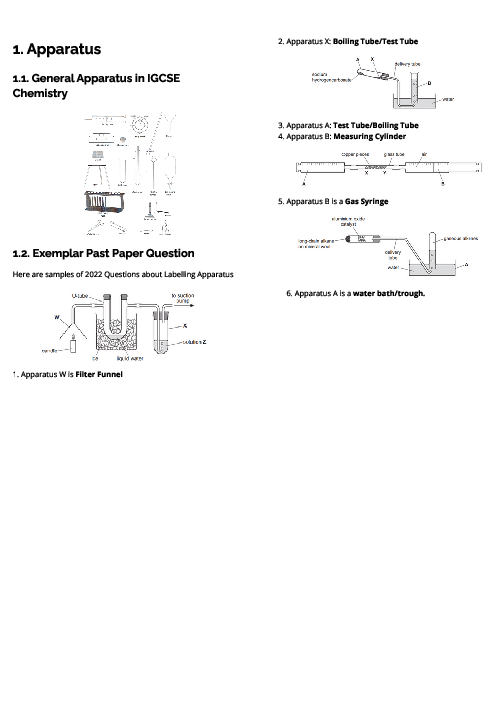
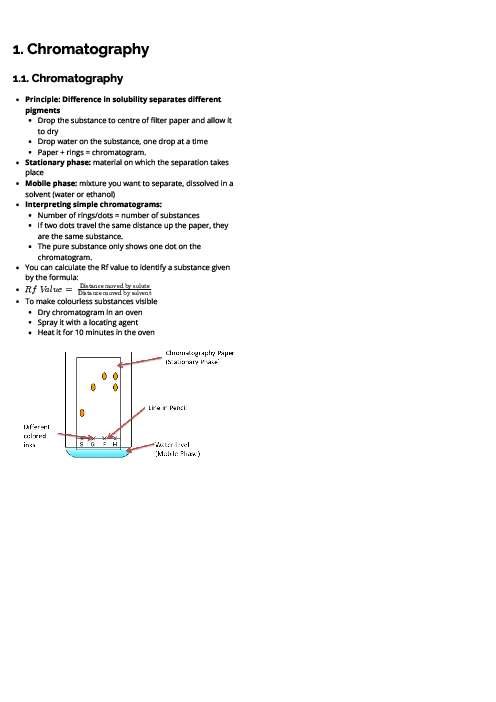
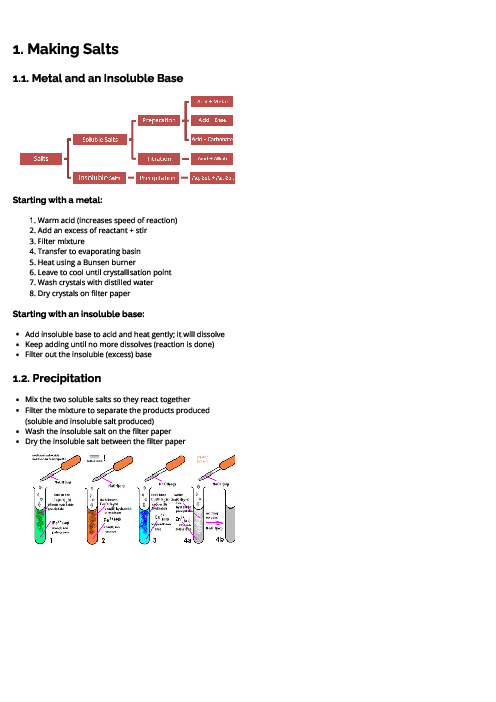
This document explains metals for CAIE IGCSE Chemistry, covering their properties, uses, reactivity, corrosion, and extraction. Physical properties of metals include high density, high melting points, good conductivity, malleability, ductility, and metallic lustre. Chemical properties include reactions with acids (forming salt and hydrogen), oxygen (metal oxides), water or steam (metal hydroxides/oxides and hydrogen). In contrast, non-metals are poor conductors, brittle, and have low melting points. The document outlines key uses of metals: aluminium (aircraft, food containers, overhead cables), zinc (galvanisation, alloys, batteries, sacrificial protection), and copper (electrical wiring). Alloys are defined as mixtures of metals (or metals and non-metals), made stronger and more corrosion-resistant than pure metals, with examples like brass (copper + zinc) and stainless steel (iron + carbon + chromium + nickel). The reactivity series is detailed from potassium to gold, explaining trends and displacement reactions. Corrosion of iron (rusting) is described, requiring water and oxygen, with prevention methods including barrier coatings and sacrificial protection (galvanisation with zinc). Extraction methods are explained: highly reactive metals (K–Al) by electrolysis, medium reactive metals (Zn–Fe–Pb) by carbon reduction, and less reactive metals (Cu, Ag, Au) occurring naturally. Detailed processes include the extraction of aluminium from bauxite using electrolysis and the blast furnace extraction of iron from haematite.
باز نشر محتواها در فضای مجازی، ممنوع است.

باز نشر محتواها در فضای مجازی، ممنوع است.