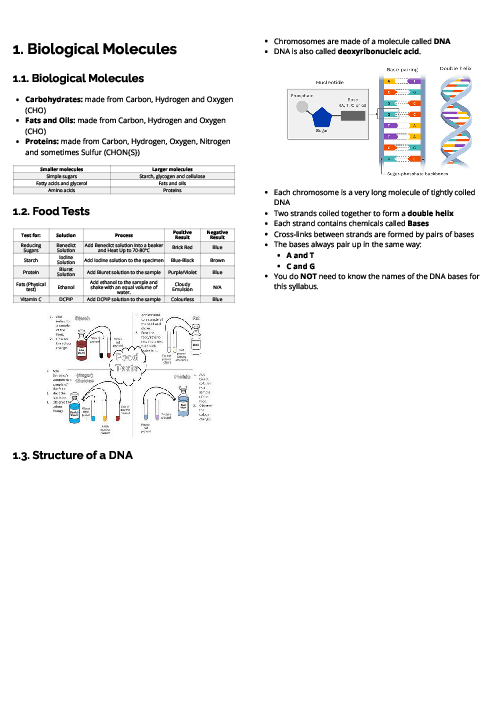
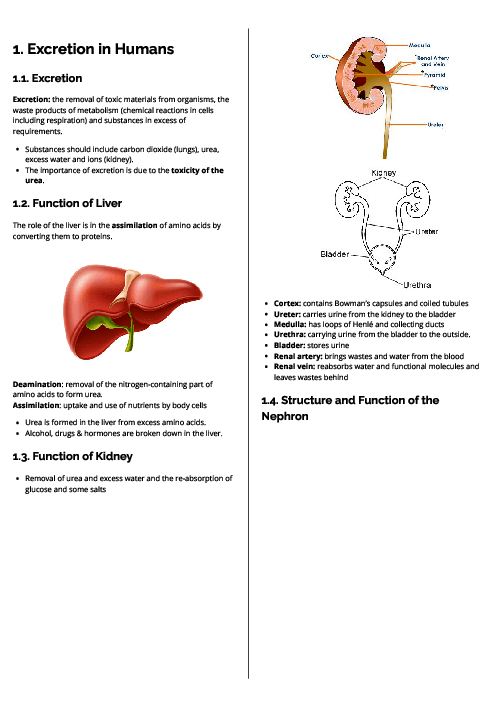
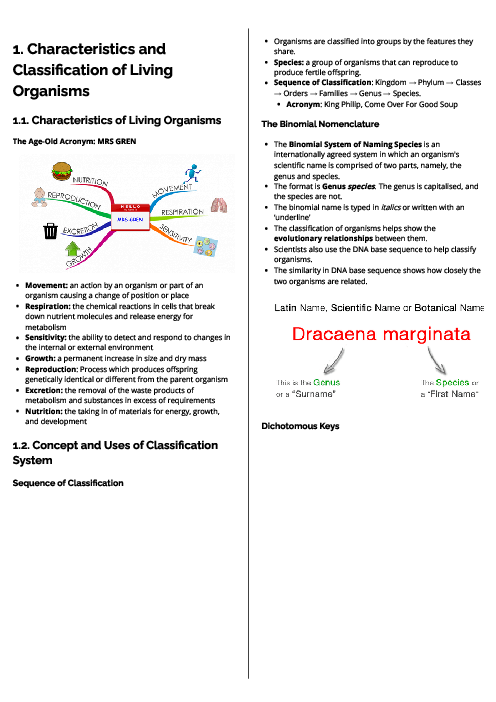
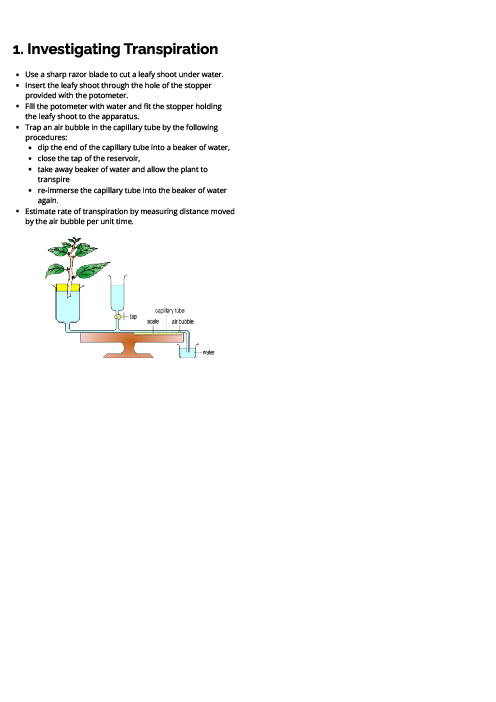
Biology (0610) Biotechnology and Genetic Modification Revision Note
This document covers biotechnology and genetic modification for CAIE IGCSE Biology. It begins by explaining why bacteria are widely used: rapid reproduction, plasmids for genetic engineering, low ethical concerns, and ability to produce complex molecules. Examples of biotechnology include biofuel production (using yeast for ethanol fermentation), bread-making (carbon dioxide from yeast respiration makes dough rise), and the use of enzymes in industry. Enzymes like pectinase extract fruit juice, proteases and lipases remove stains in biological washing powders, and lactase is used to make lactose-free milk with immobilised enzymes. The role of fermenters is explained, including conditions needed for penicillin production and large-scale culture of mycoprotein (Quorn™) as a vegetarian protein source. The section on genetic modification details altering DNA by cutting and inserting genes, such as transferring the human insulin gene into bacteria for medicine production. It also covers genetically modified (GM) crops engineered for pest resistance, herbicide resistance, improved nutrition, or drought tolerance. The advantages of GM crops include higher yields, shorter growing seasons, and reduced hunger, while disadvantages include reduced biodiversity, potential “superweeds,” and uncertain long-term effects on humans. This guide provides a clear foundation for understanding modern applications of biotechnology and genetic modification.
باز نشر محتواها در فضای مجازی، ممنوع است.
باز نشر محتواها در فضای مجازی، ممنوع است.