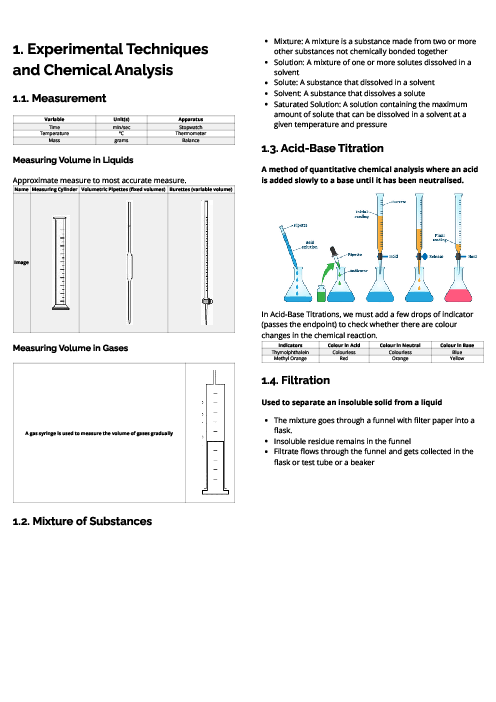
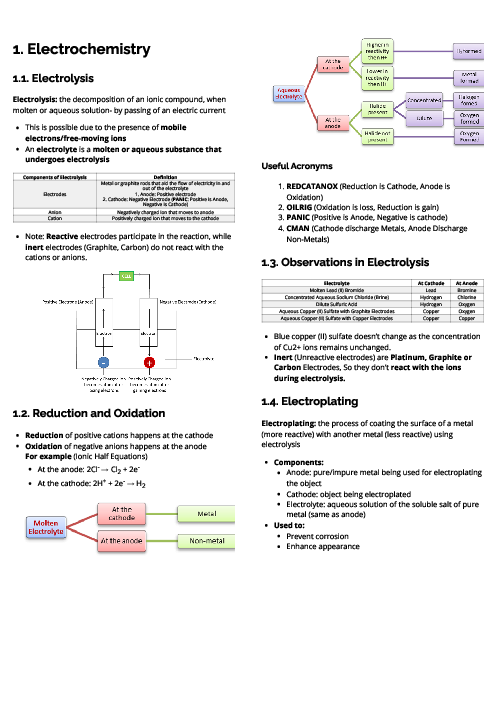
Chemistry (0620) States of Matter Revision Note
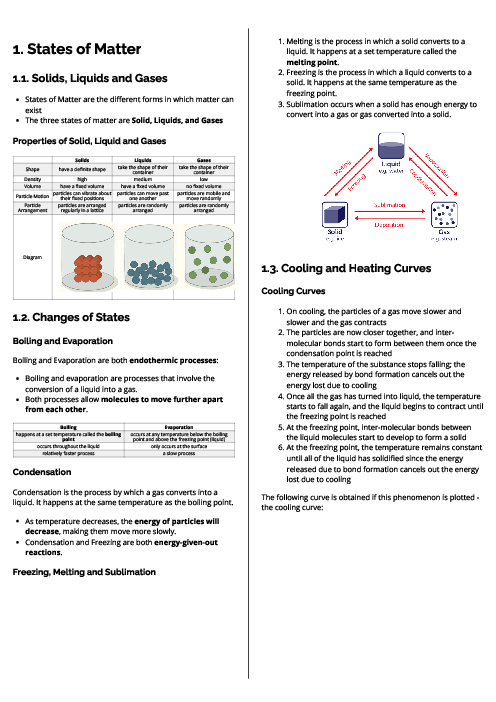
This document explains the states of matter for CAIE IGCSE Chemistry, focusing on solids, liquids, and gases and their properties. It compares their shape, density, volume, particle arrangement, and motion, showing how solids have fixed shapes, liquids take the shape of containers, and gases expand to fill space. Changes of state such as melting, freezing, boiling, condensation, evaporation, and sublimation are described, with emphasis on energy transfer and particle movement. The difference between boiling (at a fixed temperature throughout the liquid) and evaporation (at any temperature at the surface) is highlighted. Cooling and heating curves are explained step by step, showing how temperature remains constant during phase changes as energy is used to break or form intermolecular bonds. Diffusion is defined as the net movement of particles from high to low concentration, occurring fastest in gases, slower in liquids, and slowest in solids. The effect of molecular mass on diffusion is also explained: lighter molecules diffuse faster than heavier ones. The document concludes with the effect of pressure and temperature on gases, showing how changes in kinetic energy influence collisions, internal pressure, and volume. This guide gives a clear foundation for understanding particle behaviour in different states of matter.
باز نشر محتواها در فضای مجازی، ممنوع است.
باز نشر محتواها در فضای مجازی، ممنوع است.