Chemistry (0620) Organic Chemistry Revision Note
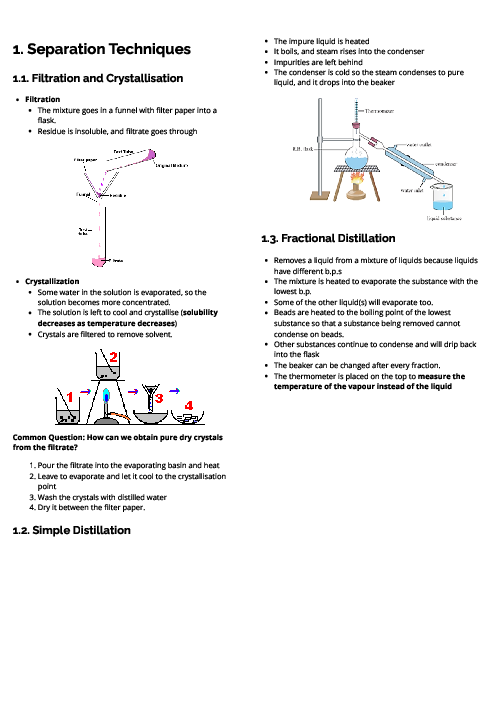
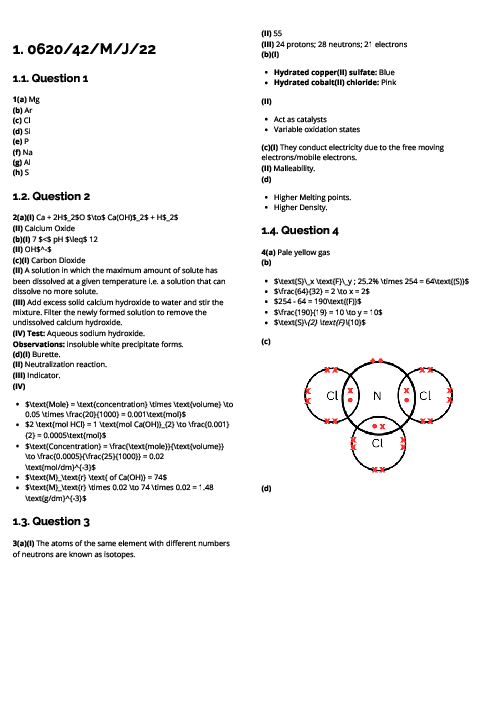
This document explains organic chemistry for CAIE IGCSE Chemistry, focusing on hydrocarbons, functional groups, and polymers. It begins with homologous series, where compounds share functional groups, general formulas, and similar chemical properties. Key series include alkanes (saturated hydrocarbons, general formula CnH2n+2), which undergo substitution under UV light; alkenes (unsaturated hydrocarbons, CnH2n), which undergo addition reactions with bromine, hydrogen, and steam; alcohols (CnH2n+1OH), produced by fermentation or hydration of ethene; and carboxylic acids (CnH2n+1COOH), weak acids formed by bacterial oxidation of ethanol or chemical oxidation. Ethanoic acid reacts with alcohols to form esters in condensation reactions. Fossil fuels like coal, natural gas, and petroleum are described, with fractional distillation separating petroleum into useful fractions. Complete combustion produces CO₂ and H₂O, while incomplete combustion produces CO, a toxic gas. Cracking of alkanes is explained as a method to produce alkenes for fuels and feedstock. The section on polymers explains addition polymerisation (e.g., poly(ethene)) and condensation polymerisation (e.g., nylon, PET), with applications in plastics, fibres, and packaging. Environmental issues of plastics, such as non-biodegradability and pollution, are also highlighted. Proteins are introduced as natural polyamides formed from amino acids. This guide provides essential foundations for understanding organic chemistry in exams.
باز نشر محتواها در فضای مجازی، ممنوع است.

باز نشر محتواها در فضای مجازی، ممنوع است.